Hi everyone I am trying to figure out exactly what diodes are and when and how they are used. Any explanation especially a detailed one would be appreciated.thanx
thanx for the reply. i read it but it still doesnt explain to me how i would wire a grand am that only has a single lock/unlock wire. how do i get the doors to unlock when i press the unlock button on the remote and so on. i see people talking about resistors and diodes and the door lock diagrams are confusing to someone who has never installed an alarm/remote start before.thanx
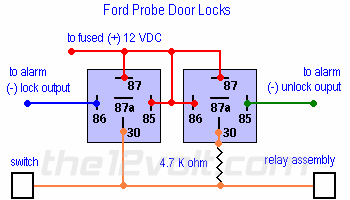
I can't find a diagram on the Grand Am, but it wires like the Ford Probe with two differences. First, instead of 87 going to 12volts they will go to ground. Second, the 4.7k resistor needs to be 1500ohm. Everything else stays the same, no diodes are needed.
-------------
Mike M2
Tech Manager
CS Dealer Services
https://www.directechs.com/techtips/pdfs/resources/security/directed_techtips/1041.pdf
I know what resistors are. But what does it do in that schematic.
Also sometimes I see resitors between 85 and 86. What is the purpose.
The item between 85 and 86 won't be a resistor it will be a diode. In order to explain it I will need to go a little more in depth.
To generate electricity, a conductor is passed through a magnetic field and depending on the size of the conductor, the strength of the magnetic field and the direction of each in relation to each other, a voltage is produced. This is power generation 101 (circuit operation will force us back here in a minute).
The second phenomenon about eletricity is that when you activate a relay (or any coil) with electricity, it builds a magnetic field around that coil (seeing the connection??); (power consumption 101).
When the power is removed from the coil (circuit), the magnetic field rapidly collapses (which immitates motion) and generates a reverse voltage within the circuit (power generation 101 in reverse). With old technology this reverse voltage could be ignored as we were dealing with large and very UN-sensitive (stable) components. With the new technology, these circuits are very sensitive and susceptible to operation by erroneous inputs due to their engineering. Diodes employed across a coil prevent this reverse voltage pulse from generating erroneous inputs by electronically shorting out the coil.
Diode theory... a diode, through it's construction, will only allow current to flow in one direction. This results in the diode appearing in the circuit one way as a broken wire and the other direction as a dead short. By installing the diode accross the coil, when energized the coil cannot see the diode but when the circuit is de-activated, the diode shorts out the reverse polarity generation and securley shuts down the relay.
More info and applications are on the links to the left under "Forums""Relays" which will lead you here https://www.the12volt.com/relays/page5.asp
